Polygonize weighted rasters
Create polygons from multiple raster layers; with nodata and scaling strategies, categorical rasters handling and arbitrary weight attributes that modifies the underlying agglomerative clustering algorithm.
Can also plot a summary of the data distributions and clustering sizes history. 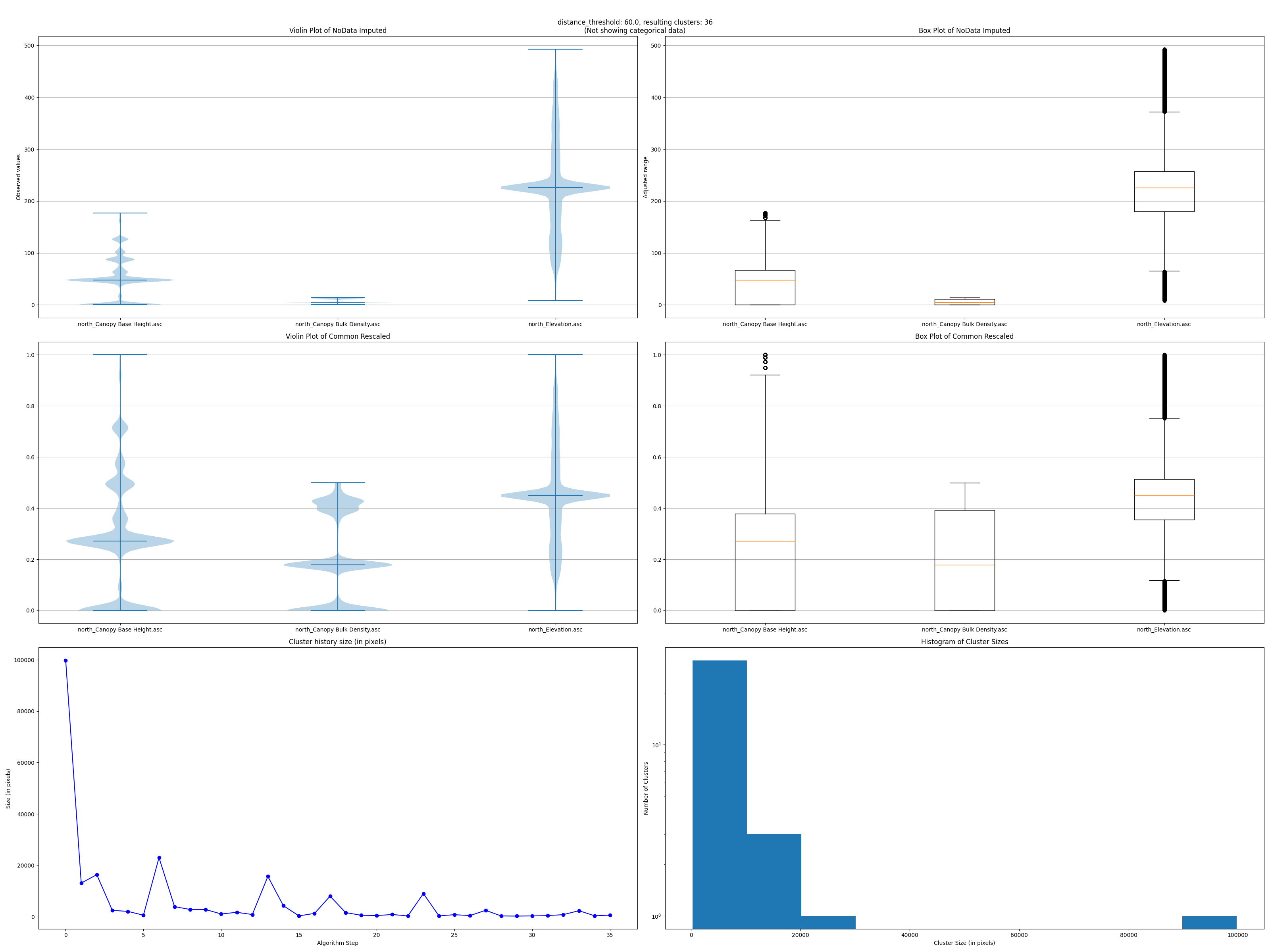
Overview
A scikit-learn pipeline that:
- Handles nodata with SimpleImputer
- Scales data with StandardScaler, RobustScaler which removes outliers or OneHotEncoder for categorical data like fuel models.
- Rescales all observations to [0, 1], then multiplies a prioritization (weight) to each raster.
- Clusterizes the map using the Agglomerative clustering algorithm.
Usage
- Select the rasters: notice you can drag & drop to reorder them.
- Optionally fill the matrix in the same order than the selected rasters, with
- scaling_strategy = [“standard”, “robust”, “onehot”] (default is “standard”)
- no_data_strategy = [“mean”, “median”, “most_frequent”, “constant”] (default is “mean”)
- fill_value = any number (only for “constant” no_data_strategy) (default is 0)
- weight = any number (default is 1) Categorical rasters (like fuel models) should use “onehot” and “most_frequent”
- Experiment with the distance threshold until you get the desired number of clusters. Less distance (until 0) yields more clusters and processing time.
-
Fine tune the output, ensuring clusters have a minimum number of pixels using the advanced parameter -that invokes GDAL’s: gdal_sieve
- Outputs: The output polygon layer has the attribute ‘number of pixels’. The raster layer can be skipped.
- Data debug: There’s an additional option to raise a (mat)plot(lib) window with original & rescaled data distributions, clustering sizes history & histogram labels. Available outside QGIS, by executing the shown command adding the ‘–plots’ flag in the terminal (OSGeo4WShell).
In depth documentation and source code can be found here